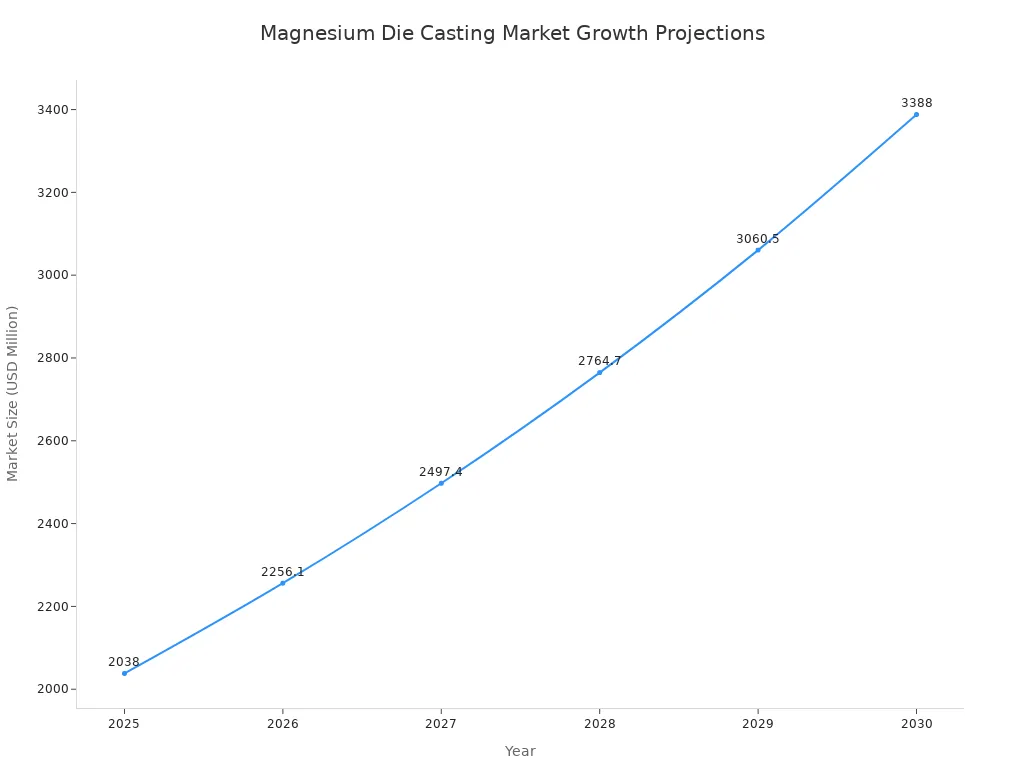
Magnesium finds extensive application in die casting processes. Its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, excellent castability, and superior thermal and electrical conductivity make it ideal for lightweight, high-performance components across various industries. Manufacturers increasingly choose magnesium for these benefits. The automotive parts Magnesium Die Casting market shows significant growth. It projects an increase from USD 2,038 million in 2025 to USD 3,750 million in 2031, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 10.7% from 2025 to 2034. This growth highlights increased adoption where magnesium used in manufacturing is critical.
Key Takeaways
- Magnesium is the lightest structural metal. It helps make products much lighter.
- Magnesium flows easily when melted. This helps create complex and thin parts quickly.
- Magnesium parts are strong for their weight. They also reduce noise and protect electronics.
- New treatments make magnesium more resistant to rust. This helps it last longer in tough places.
- Magnesium is common and easy to recycle. It saves energy when made and used in products.
- Magnesium helps vehicles use less fuel. It also makes portable electronics work better.
- Magnesium can have many surface finishes. These finishes make parts look good and work well.
Unmatched Lightweight Properties: Why Magnesium is Used for Weight Reduction

Superior Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Lightest Structural Metal
Magnesium alloys are recognized for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratios. They represent the lightest structural metal available for engineering applications. Magnesium possesses a specific gravity of 1.74. Its typical density ranges from 1.75 to 1.85 grams per cubic centimeter. This density compares favorably to aluminum alloys, which typically range from 2.5 to 3.0 grams per cubic centimeter. This inherent lightness makes magnesium an ideal choice for applications requiring minimal mass without compromising structural integrity.
Significant Mass Reduction
Manufacturers achieve significant mass reduction by incorporating magnesium components into their designs. Precipitation-hardened magnesium alloys exhibit a strength-to-weight ratio comparable to strong aluminum alloys. Magnesium’s lower density (approximately 1.8 g/cm³) contributes significantly to this advantage compared to aluminum (approximately 2.8 g/cm³). While the mechanical properties of magnesium alloys generally fall below the absolute strongest aluminum alloys, rapidly solidified magnesium powders can achieve tensile strengths up to 740 MPa. This strength is comparable to the strongest aluminum alloys. This capability allows engineers to design parts that are both exceptionally light and remarkably robust, leading to innovative product develoPment across various sectors.
Fuel Efficiency and Performance Benefits
Improved Vehicle Fuel Economy
The automotive industry extensively utilizes magnesium for weight reduction. Lighter vehicle components directly translate into improved fuel economy and reduced emissions. Every kilogram reduced in a vehicle contributes to lower fuel consumption and decreased environmental impact. Magnesium die-cast parts, such as transmission casings, engine blocks, steering wheel armatures, and interior frames, significantly decrease the overall vehicle weight. This reduction helps automakers meet stringent environmental regulations and satisfy consumer demands for more efficient and sustainable transportation. The adoption of lightweight magnesium components also enhances vehicle handling and acceleration, contributing to a better driving experience.
Enhanced Portable Electronics Performance
Portable electronics also benefit greatly from magnesium’s lightweight properties. Devices like laptops, smartphones, tablets, and cameras require durable yet extremely light enclosures. Magnesium alloys provide the necessary structural integrity and rigidity without adding excessive bulk. This allows for sleeker designs, improved ergonomics, and easier portability for consumers. The material’s excellent thermal conductivity also contributes to the longevity and stable performance of electronic components by efficiently dissipating heat. Therefore, magnesium used in these applications enhances both user experience and extends product lifespan, making it a preferred material for high-performance gadgets.
Excellent Castability and Production Efficiency: Why Magnesium is Used for Complex Parts

High Fluidity for Complex Geometries
Fills Intricate Die Cavities
Magnesium alloys exhibit exceptional fluidity when molten. This characteristic allows the liquid metal to flow easily into intricate die cavities. It effectively fills complex shapes and fine details within the mold. This high fluidity ensures the production of parts with precise dimensions and elaborate designs, which would be challenging or impossible with less fluid materials. Manufacturers can achieve highly detailed components without compromising structural integrity.
Enables Thin-Walled Parts
The superior fluidity of magnesium also enables the creation of very thin-walled components. Designers can specify wall thicknesses as low as 0.8 mm for certain applications. This capability is crucial for reducing overall part weight while maintaining strength and rigidity. Thin-walled magnesium parts are particularly valuable in industries like automotive and electronics, where space and weight are critical design considerations. This allows for innovative product designs and further weight savings.
Rapid Solidification and Cycle Times
Shorter Production Cycles
Magnesium alloys possess a low latent heat of fusion and high thermal conductivity. These properties contribute to rapid solidification once injected into the die. The quick cooling process significantly shortens the overall production cycle time for each part. This efficiency allows manufacturers to produce more components in less time, increasing throughput and operational speed.
Lower Manufacturing Costs
The rapid solidification and shorter production cycles directly translate into lower manufacturing costs. Faster cycles mean less energy consumption per part and more efficient use of machinery and labor. This economic advantage makes magnesium die casting a cost-effective solution for high-volume production. The efficiency gained helps reduce the overall unit cost of components, benefiting both manufacturers and consumers.
Reduced Tool Wear
Less Abrasive on Molds
Magnesium alloys are generally less abrasive than other common die-casting materials, such as aluminum. Their inherent material properties cause less friction and wear on the steel molds during the injection and ejection processes. This reduced abrasiveness helps preserve the integrity of the die.
Extended Die Life
The decreased wear on molds directly leads to an extended die life. Dies are expensive tools, and their longevity significantly impacts manufacturing costs. When magnesium is used in die casting, the molds last longer, requiring less frequent replacement or refurbishment. This reduces tooling expenses and minimizes production downtime, further enhancing the overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the die-casting process.
Desirable Mechanical and Physical Properties: Why Magnesium is Used for Performance
High Specific Strength and Stiffness
Magnesium alloys offer an excellent combination of specific strength and stiffness. This makes them highly desirable for various performance-critical applications.
Robust Performance for Structural Applications
Magnesium provides robust performance for structural applications. Its high strength-to-weight ratio allows engineers to design components that are both light and strong. This is crucial in industries like aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment. These sectors demand materials that can withstand significant loads without adding excessive mass. Magnesium components contribute significantly to overall structural integrity and operational efficiency.
Maintains Integrity Under Stress
Magnesium alloys maintain their integrity well under stress. They resist deformation and fracture even when subjected to considerable forces and varying temperatures. For example, a recently developed die-cast magnesium alloy, Mg-RE-Al, demonstrates a yield strength of 94 MPa and a tensile strength at temperatures up to 300°C. This represents a 42% improvement over the next best high-temperature die-cast magnesium alloy in terms of stable stiffness under extreme conditions. This capability ensures the reliability and safety of parts in demanding environments, making magnesium use in critical structural components.
Good Damping Capacity
Magnesium possesses excellent damping capacity. This property allows it to absorb vibrational energy effectively.
Reduces Noise and Vibration
Magnesium components significantly reduce noise and vibration in mechanical systems. This is particularly beneficial in applications where smooth, quiet operation is essential. Examples include engine mounts, gearboxes, and machinery housings. The material converts vibrational energy into heat, dissipating it before it can propagate through the system. This leads to quieter environments and more comfortable user experiences in various products.
Improves Component Longevity
The ability to dampen vibrations also improves component longevity. Excessive vibration can cause fatigue, wear, and premature failure in parts. By absorbing these stresses and reducing resonant frequencies, magnesium helps extend the operational life of components. This reduces maintenance needs, lowers replacement costs, and enhances the overall reliability of the system over time.
Electromagnetic Shielding
Magnesium offers inherent electromagnetic shielding properties. This makes it a valuable material for protecting sensitive electronic devices.
Protects Sensitive Electronics
Magnesium enclosures effectively block electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). This shielding prevents external signals from disrupting internal electronics. It also stops internal signals from interfering with other nearby devices. This protection is vital for the reliable and stable operation of modern electronic equipment, especially in environments with high electromagnetic noise.
Ideal for Enclosures
Magnesium is an ideal material for electronic enclosures. Its superior shielding capabilities, combined with its lightweight nature and good thermal conductivity, make it a preferred choice. Many portable electronic devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and medical instruments, use magnesium housings. The material ensures both robust physical protection and excellent electromagnetic compatibility. This dual benefit enhances product performance, extends device lifespan, and improves user satisfaction.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Efficient Heat Dissipation
Magnesium alloys possess excellent thermal conductivity. This property allows them to efficiently transfer heat away from critical components. This is vital for maintaining optimal operating temperatures in many devices. For example, in electronics, effective heat dissipation prevents overheating. This extends the lifespan and ensures stable performance of sensitive circuits. High thermal conductivity is particularly beneficial for microprocessors and power modules. These components generate significant heat during operation. The automotive industry also benefits significantly. Magnesium engine parts, such as transmission casings and engine blocks, can manage heat effectively. This improves engine efficiency and durability. This capability is crucial for high-performance applications where thermal management is paramount. Efficient heat transfer prevents thermal stress and material degradation. It also contributes to the overall reliability of the system. The selection of a specific magnesium alloy often depends on the required thermal performance.
Here is a comparison of thermal conductivity values for common magnesium die-casting alloys:
| Alloy | Thermal Conductivity (W/(m·K)) |
|---|---|
| AZ91D | 51.2 |
| AS21 | 68 |
| Mg–3RE–0.5Zn (EZ30) | Not specified, but designed for superior thermal conductivity |
| Mg–7Al–3Ca (AX73) | 67 (as-cast), 68.5 (aged) |
| Mg–2Mn–xLa | 135 |
| Mg–3Zn–0.5Ca–0.5Al–1Mn | 133 |
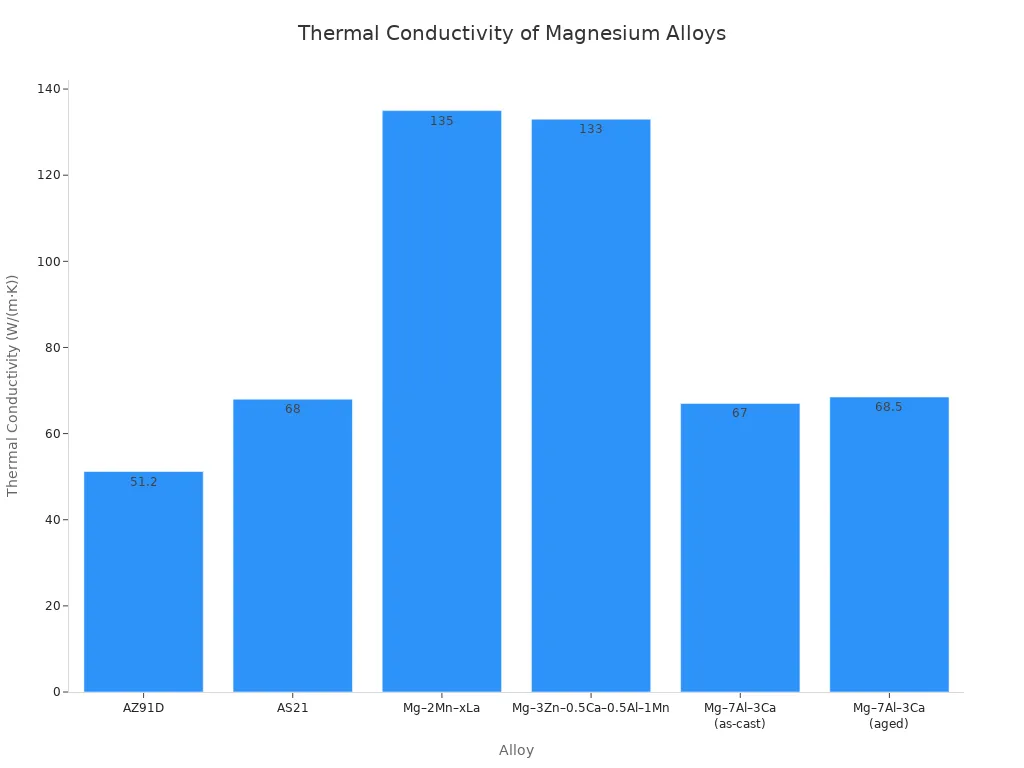
The chart visually represents these differences. Alloys like Mg–2Mn–xLa and Mg–3Zn–0.5Ca–0.5Al–1Mn show particularly high thermal conductivity. This makes them ideal for applications requiring rapid heat transfer. Engineers carefully select specific magnesium alloys based on the thermal demands of the component. This ensures efficient operation and prevents thermal degradation. This property is a key factor in designing compact and powerful electronic devices. It allows for smaller form factors without compromising thermal management.
Suitable for Electrical Components
Magnesium also exhibits good electrical conductivity. This characteristic, combined with its lightweight nature and electromagnetic shielding capabilities, makes it highly suitable for various electrical components. Manufacturers frequently use magnesium in housings for portable electronics. It provides both structural integrity and efficient electrical grounding. This helps protect internal circuitry from external interference. The material’s ability to conduct electricity also supports its use in certain electrical connectors or heat sinks. These components require both thermal and electrical performance. The combination of these properties enhances the overall functionality and reliability of electronic devices. For instance, in telecommunications equipment, magnesium enclosures offer a robust yet light solution. They effectively manage heat and shield sensitive electronics. This dual benefit ensures optimal performance in demanding environments. The versatility of magnesium used in these applications highlights its value in modern engineering. Its electrical properties contribute to the overall efficiency of power transmission within devices. This makes it a strategic material for advanced technical products. This includes components in electric vehicles where efficient power distribution and thermal management are critical.
Corrosion Resistance and Surface Treatment: Why Magnesium is Used in Demanding Environments
Improved Corrosion Resistance
Magnesium’s inherent reactivity once presented challenges for its widespread use. However, significant advancements have dramatically improved its corrosion resistance. These developments make magnesium suitable for demanding environments.
Advances in Alloy Development
Researchers have made substantial progress in developing new magnesium alloys. Strategic alloying involves incorporating elements like rare earth or zinc. These additions control degradation rates. Advanced surface modification techniques also play a crucial role. Methods such as plasma electrolytic oxidation and bioactive coatings enhance corrosion resistance. They also improve biocompatibility. Innovative fabrication methods, like additive manufacturing (e.g., selective laser melting, laser powder bed fusion), create complex structures. These structures have controlled porosity and improved mechanical durability. Specific alloy systems, such as Mg-2Zn-0.5Ca and magnesium-lithium alloys, demonstrate reduced degradation rates. They also maintain mechanical integrity. These innovations ensure magnesium components perform reliably in harsh conditions.
Protective Coatings and Treatments
Beyond alloy development, various protective coatings and treatments further enhance magnesium’s resistance to corrosion. These surface treatments create a barrier between the metal and the environment. They prevent corrosive agents from reaching the magnesium surface. Common methods include conversion coatings, anodizing, and electroplating. These treatments not only protect the material but also prepare it for subsequent finishing processes. They ensure long-term durability and performance in diverse applications.
Enhanced Surface Finish
Magnesium die castings can achieve a wide range of surface finishes. These finishes serve both aesthetic and functional purposes.
Aesthetic Appeal
Achieving an attractive surface finish is crucial for many consumer products. Mechanical finishing methods, such as post-trim deburring, round sharp edges, and remove burrs. They also smooth and brighten surfaces. Surface conversion coatings remove contaminants and can act as a primer or final finish. Environmentally friendly trivalent clear chromium offers high corrosion resistance and a bright finish. Combined conversion coatings and functional finishes provide increased corrosion protection or a semi-decorative appearance. A final cosmetic surface finish is chosen for aesthetics. It maximizes corrosion resistance and improves heat dissipation. Electro-deposition offers the most attractive, durable, and wear- and corrosion-resistant finish. Chemical treatments like anodizing create a hard, corrosion-resistant coating. Chromate conversion coating is used as an undercoat for paint adhesion or standalone corrosion protection. Painting and plating options offer versatile solutions for enhancing appearance.
Functional Surface Properties
Surface treatments do more than just improve appearance. They also impart critical functional properties to magnesium components. Anodizing, for example, creates a hard, corrosion-resistant layer. Specific treatments like Chemical Treatment No. 9, No. 17, HAE, and Cr-22 enhance this protection. Electro-deposition also enhances EMI-RFI shielding. This is vital for electronic enclosures. These functional finishes improve durability and surface performance. They can also add insulation. The ability to tailor surface properties makes magnesium a versatile material for various applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Sustainability: Why Magnesium is Used for Economic and Environmental Benefits
Material Abundance and Recyclability
Magnesium offers significant advantages in terms of material availability and its potential for recycling. These factors contribute to its economic viability and environmental sustainability.
Readily Available Element
Magnesium is one of the most abundant elements on Earth. It constitutes about 2% of the Earth’s crust. It is also the third most common structural metal in the crust. Furthermore, seawater contains vast quantities of magnesium. This widespread availability ensures a stable and long-term supply for industrial applications. Its natural abundance reduces concerns about resource depletion. This makes magnesium a sustainable choice for manufacturing processes.
High Recyclability Rate
Magnesium alloys boast a high recyclability rate. Manufacturers can remelt and reuse magnesium scrap from production processes and end-of-life products. This recycling process requires significantly less energy than producing primary magnesium from raw materials. High recyclability minimizes waste. It also reduces the environmental impact associated with mining and refining new resources. This closed-loop material cycle enhances the overall sustainability profile of magnesium die casting.
Energy Savings in Production and Use
Magnesium contributes to energy savings throughout its lifecycle, from manufacturing to end-product use.
Lower Melting Point Reduces Energy
Magnesium has a relatively low melting point compared to other common die-casting metals like aluminum. Its melting temperature is approximately 650°C, while aluminum melts around 660°C. This lower melting point translates directly into reduced energy consumption during the casting process. Foundries require less energy to heat and maintain molten magnesium. This decreases production costs and lowers the carbon footprint of manufacturing magnesium components.
Lightweight Products Save Operational Energy
The lightweight nature of magnesium components leads to substantial energy savings in their operational phase. In the automotive industry, lighter vehicles consume less fuel. This reduces greenhouse gas emissions. For portable electronic devices, lighter components extend battery life. This improves user convenience and reduces the frequency of charging. These operational energy savings provide long-term economic and environmental benefits. They make magnesium an attractive material for industries focused on efficiency and sustainability.
Magnesium’s unique combination of lightweight properties, superior castability, excellent mechanical characteristics, and cost-effectiveness establishes it as the material of choice for die casting. These attributes collectively enable the production of high-performance, lightweight, and complex components. Magnesium used in these applications is essential for various advanced industries.
FAQ
What makes magnesium ideal for lightweight components?
Magnesium is the lightest structural metal. It offers an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. This allows for significant mass reduction in products. Its use improves fuel efficiency in vehicles and enhances performance in portable electronics.
How does magnesium’s castability benefit manufacturing?
Magnesium exhibits high fluidity when molten. This property allows it to fill intricate die cavities and create complex, thin-walled parts. It also solidifies rapidly, leading to shorter production cycles and lower manufacturing costs.
What mechanical properties does magnesium offer for performance?
Magnesium provides high specific strength and stiffness, ensuring robust performance in structural applications. It also has good damping capacity, which reduces noise and vibration. Furthermore, it offers electromagnetic shielding for sensitive electronics.
Is magnesium resistant to corrosion?
Advances in alloy development and surface treatments have significantly improved magnesium’s corrosion resistance. Protective coatings and specialized treatments create barriers against corrosive elements, making it suitable for demanding environments.
How does magnesium contribute to sustainability?
Magnesium is an abundant element with a high recyclability rate. Its lower melting point reduces energy consumption during production. Lightweight magnesium components also save operational energy in vehicles and electronics, promoting overall sustainability.
Can magnesium be used for electrical components?
Yes, magnesium possesses good electrical conductivity. This, combined with its lightweight nature and electromagnetic shielding, makes it suitable for various electrical components. It provides efficient grounding and protects internal circuitry.
What surface finishes can magnesium die castings achieve?
Magnesium die castings can achieve various aesthetic and functional surface finishes. These include mechanical finishes, conversion coatings, anodizing, and electroplating. These treatments enhance appearance, corrosion resistance, and other functional properties.

